What Sets Industrial-grade DRAM Modules Apart?
Article By : Apacer

Industrial-grade devices are often tasked with operating in challenging environments. These can include extreme temperature changes, high humidity, extensive dust, various kinds of pollution, and vibrations or shocks.
An Examination of the DRAM IC Grade
As the 5G era dawns, the market penetration of the Intelligent Internet of Things (IIoT), autonomous vehicles and Internet of Vehicles (IoV) applications will accelerate. In order to keep up with the associated demand for data storage, transmission and computing power in the future, industrial installations such as data centers, servers and even edge computing devices are expected to replace traditional mobile devices and become the key drivers of the DRAM industry.
The role of real-time data is becoming more and more important, and DRAM’s benchmarks for durability and reliability are increasing rapidly. Yet some system integrators are making the mistake of incorporating commercial-grade DRAM modules into their industrial-grade devices. The result will inevitably be lost or damaged data, and a shortened operational lifetime for the device itself. With this in mind, it’s important to examine what sets industrial-grade DRAM modules apart from commercial grade. The first issue to investigate is the DRAM IC grade.
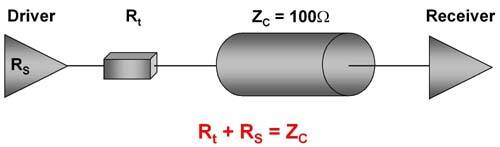
Identifying DRAM IC Chip Grade by Appearance
Generally speaking, DRAM ICs can be divided into four grades. The quality level, from high to low, is as follows: Major ICs, eTT, uTT, and downgrade.
-
Major (Original brand DRAM ICs): manufactured by DRAM makers, using the best quality wafers, and following the original factory’s comprehensive testing procedures, ICs will be printed with the manufacturer's trademarks, such as Samsung, Micron, SK Hynix and so on. Users can clearly identify the specifications and manufacturers of the IC and enjoy the advantages of the manufacturer’s warranty.
-
eTT (Effectively tested DRAM): DRAM ICs that have been tested for effectiveness, but have not been fully tested, are of lower quality than the major-grade DRAM IC. It’s primarily downstream DRAM module makers that buy these ICs and attach their own trademarks to them.
-
uTT (Untested DRAM): refers to the DRAM ICs without any test after packaging. The quality is usually more doubtful. They are also purchased by downstream DRAM module manufacturers and printed with various trademarks.
-
Downgrade: Made from wafers and dies with poor yields, and mixed with ICs that have not been screened or tested. This may even include ICs that have failed tests at higher certification levels. This level of IC often has serious compatibility issues and high defect rates, and cannot meet most quality requirements.
DRAM IC: The Decisive Element of Memory Module Reliability
It’s common for commercial DRAM modules manufacturers to use eTT, uTT and even downgrade ICs, especially when it comes to price-conscious consumer goods or low-end applications. As eTT, uTT and downgrade ICs are all printed with the trademarks of DRAM modules manufacturers and look confusingly similar, it’s even harder for clients and purchasers to distinguish these three kinds of ICs and identify the quality of DRAM ICs.
Obviously, high-end industrial applications can’t afford to accept the risk of unexpected shutdowns due to faulty or unreliable DRAM modules. Purchasing industrial-grade DRAM modules made with original DRAM ICs from major manufacturers may cost more, but it also offers the highest grade of reliability and quality. If, by some chance, there’s a problem with an industrial-grade DRAM module, the warranty protection ensures that failure analysis will determine the cause of the problem and a solution will be developed.
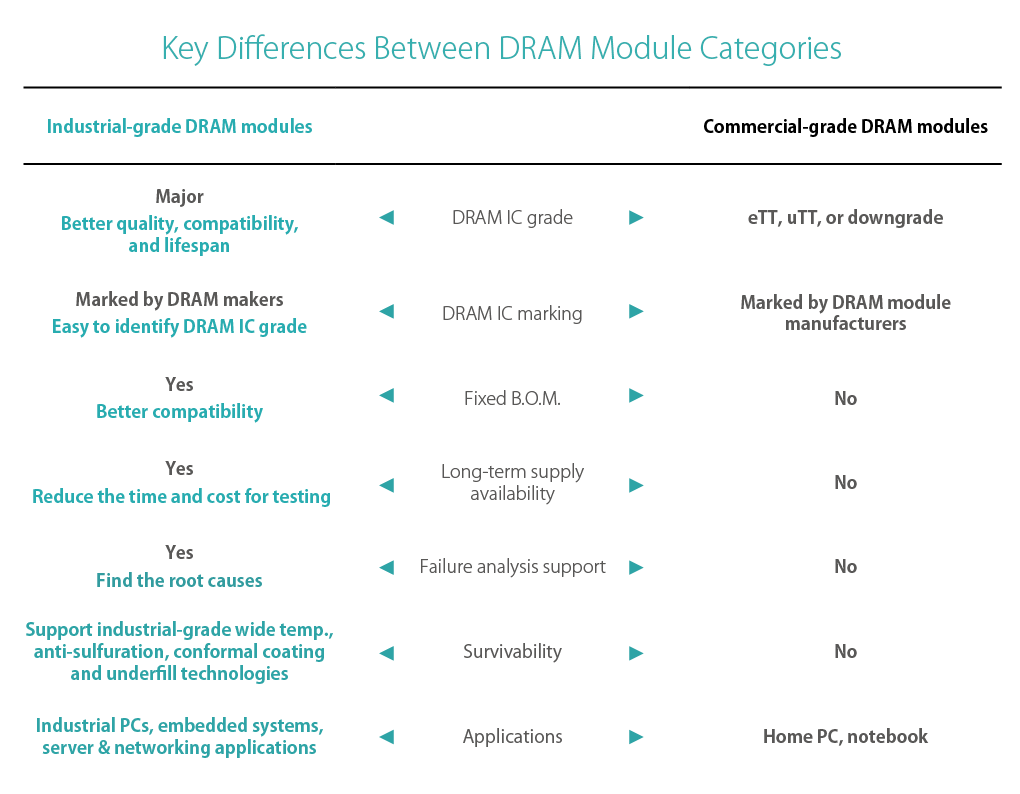
Value-adding Technologies, Rigorous Testing and Fixed B.O.M. Make Industrial-grade DRAM modules Indispensable
Industrial-grade devices are often tasked with operating in challenging environments. These can include extreme temperature changes, high humidity, extensive dust, various kinds of pollution, and vibrations or shocks. With these conditions in mind, industrial-grade DRAM modules incorporate certain value-adding features, such as wide temperature operation ranges, 30 μ gold plating, conformal coating, anti-sulfuration and underfill technology.
To further ensure their reliability, industrial-grade DRAM modules are subjected to extensive testing. Common tests include high/low temperature tests, temperature cycling tests, power cycling tests, shock/vibration tests and ongoing reliability tests. What’s more, Commercial-grade DRAM modules sometimes swap out certain ICs in the manufacturing process, which could cause serious quality, stability and compatibility problems down the line. Conversely, as the DRAM modules are required to go through a long-time testing and verification before being adopting in industrial derives, industrial-grade DRAM manufacturers usually offer long-term supply service and Fixed B.O.M. solutions to reduce the risk of revalidation and additional manpower cost.
For consumer products, cost-effectiveness is the overriding consideration. Conversely, industrial-grade devices have extremely high standards for quality, reliability and stability from materials selection, production, testing and quality control.
In the modern world, Apacer has emerged as a leading supplier of industrial-grade DRAM modules, sourcing ICs directly from their original manufacturers and developing many value-adding features in-house. In 2019, the industrial-grade product identification “Apacer for Industrial” has launched. Choose Apacer’s DRAM modules if you’re searching for high-quality, high-reliability, high-endurance industrial grade products.
Subscribe to Newsletter
Test Qr code text s ss